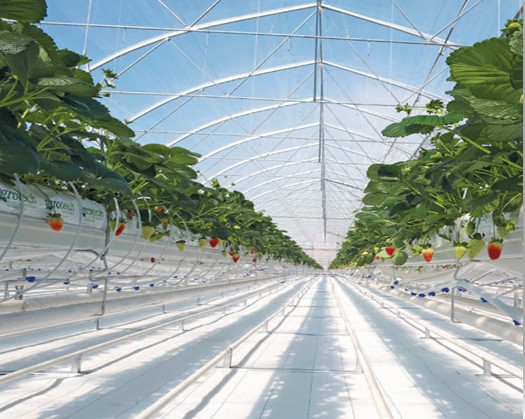
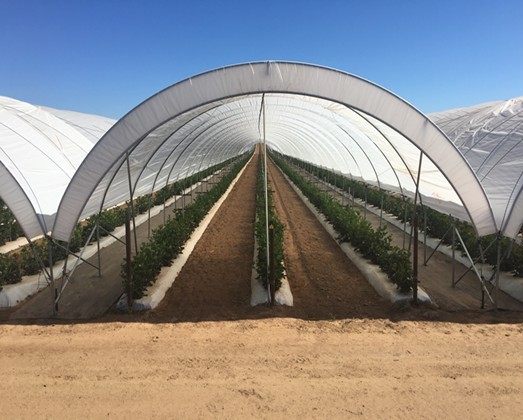


Introduction
Greenhouses, hoop houses, and poly-tunnels have become essential tools for growers worldwide. At the heart of these structures lies one key innovation: multi-layer plastic films. Unlike simple single-layer covers, these advanced materials are engineered to protect crops, optimize growth conditions, and extend the durability of the cover itself.
How Multi-Layer Plastic is Made
1. Extrusion Process
Multi-layer greenhouse films are produced using a process called co-extrusion. In this method, pellets of polyethylene and other polymers are melted and forced through extruder machines. Each extruder produces a thin molten sheet of plastic.
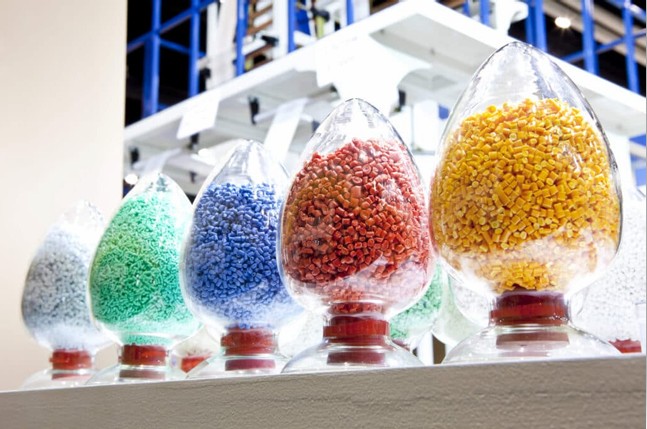
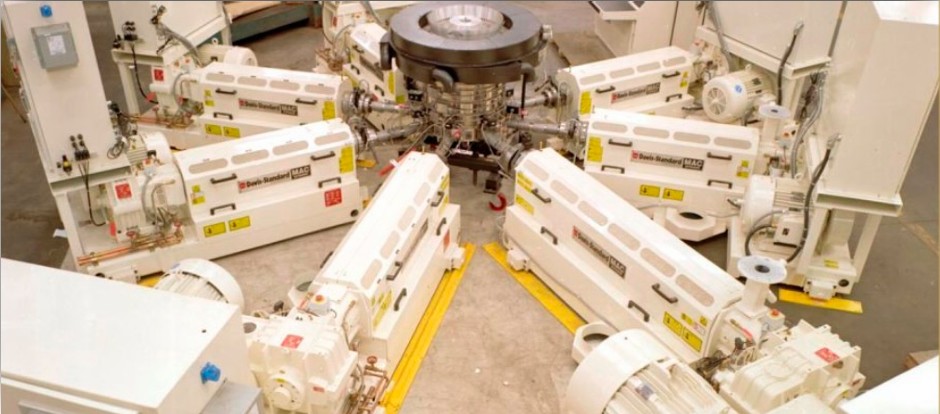
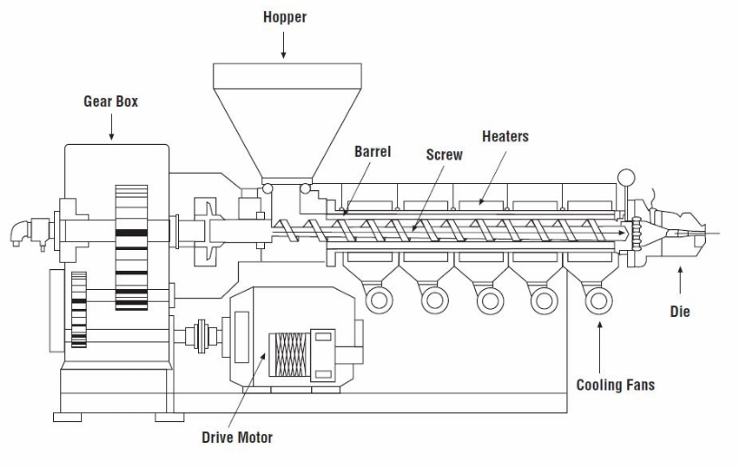


2. Forming the Film
The molten plastic layers are combined in a circular die head, forming a continuous bubble of plastic. Air pressure inflates this bubble upward, while rollers stretch and flatten it into a thin sheet.
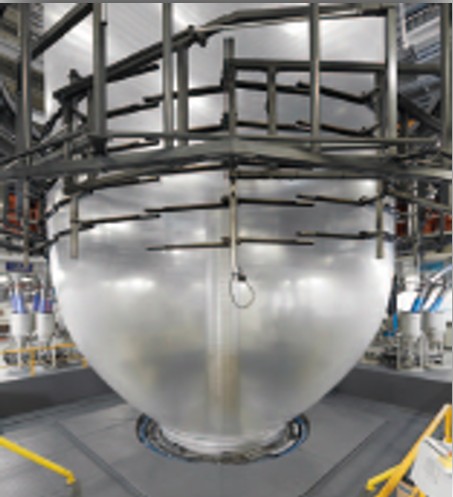

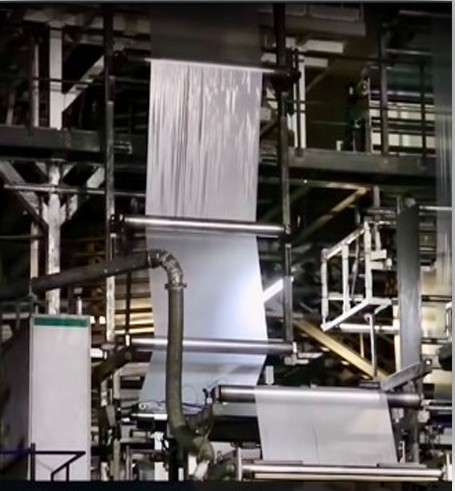
3. Rolling & Packaging
Once cooled and flattened, the multi-layer sheet is rolled into giant spools. These rolls can later be cut and applied to greenhouses or tunnels of all sizes.


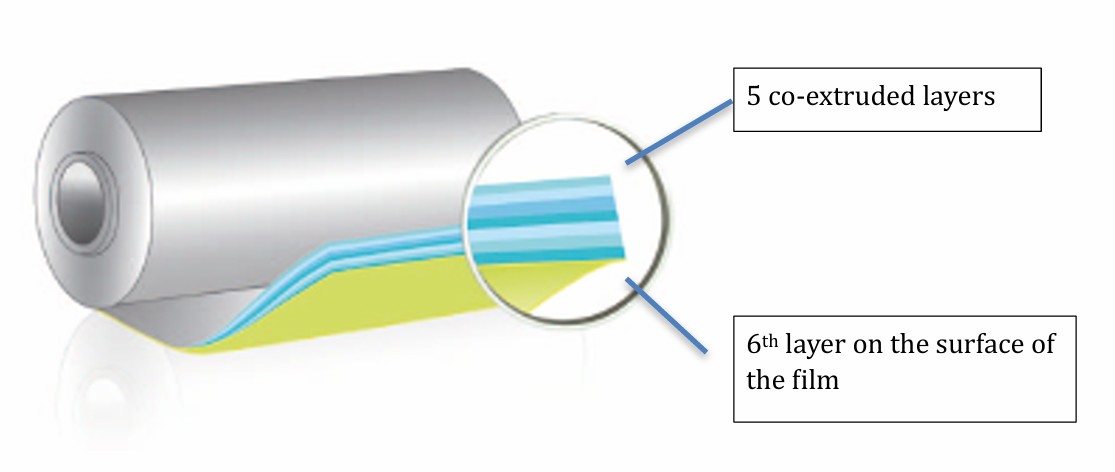
Why Multi-Layer Matters
Each layer in the film serves a specific function, and when combined, they create a high-performance material greater than the sum of its parts.
1. UV Protection Layer - Shields crops and plastic from damaging solar radiation.
2. Thermal Layer - Reduces nighttime heat loss and stabilizes the greenhouse climate.
3. Anti-Drip / Anti-Fog Layer - Prevents condensation and maintains light transmission.
4. Light Diffusion Layer - Scatters sunlight evenly, reducing plant stress.
5. Strength Layer - Provides mechanical durability against wind and tension.
Benefits to Growers
- Extended film lifespan: up to 4-5 years in tough climates.
- Better crop yields through more consistent micro-climates.
- Lower energy use due to improved heat retention.
- Reduced disease risk from less condensation.
Conclusion
Multi-layer greenhouse films represent the intersection of material science and agriculture. By combining multiple polymer layers, manufacturers can engineer various plastic types to accommodate individual micro-climates and associated crop types. Choosing the right greenhouse plastic can significantly affect crop yields, lower operational costs and increase your bottom line. Make sure to consult an experienced provider for the option that best suits your individual needs.